The Future of Data Cabling: Trends to Watch in Structured Networking
the top trends shaping the future of data cabling and structured networking, including PoE, fiber optics, modular systems, and smart building integration.
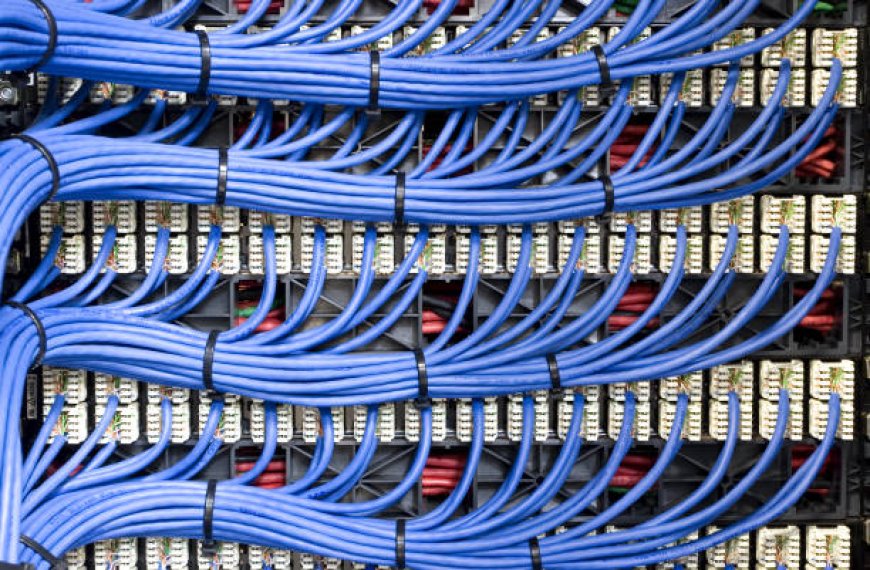

As technology continues to evolve, structured networking has become the backbone of communication for businesses, educational institutions, and even smart homes. With the surge in data consumption, video conferencing, cloud computing, and IoT devices, the role of high-quality data cabling has gained even more importance. Structured cabling is no longer just a technical necessity; it's a strategic investment in infrastructure that determines speed, reliability, and future scalability.
Cabling systems, which were once relatively straightforward, are now adapting to growing demands in bandwidth and device connectivity. The future of structured networking depends significantly on the advancements made in data cabling, both in terms of material quality and installation practices. Lets explore the key trends shaping this future and what they mean for installers, engineers, and end-users alike.
Increasing Demand for High-Speed Connectivity
One of the most influential factors driving the future of data cabling is the increasing need for faster network speeds. With the rise of 4K video streaming, high-frequency trading, remote work, and artificial intelligence applications, networks must support faster data transmission with minimal latency.
This demand is pushing the shift from Cat5e and Cat6 cables to Cat6a, Cat7, and even Cat8 cabling systems. These newer categories support higher bandwidth and frequencies, which means they can handle more data with greater efficiency. For example, Cat8 cables are designed to support speeds of up to 40Gbps at short distances, which is especially useful in data centers and enterprise environments.
Integration with Smart Building Infrastructure
The future of structured networking is closely tied to the development of smart buildings. Modern commercial and residential buildings are being designed with automation systems that manage lighting, HVAC, security, and energy consumption. All of these systems require reliable cabling that can facilitate communication between various devices and systems.
Low-voltage cabling systems are now being integrated with building management systems from the design phase. This means that data cabling is no longer considered a secondary feature but a fundamental aspect of architecture. As more buildings become smart-enabled, the demand for versatile and high-capacity cabling will continue to grow.
PoE (Power over Ethernet) Becoming Standard
Power over Ethernet technology allows electrical power and data to be transmitted through the same Ethernet cable. This simplifies installations for devices like IP cameras, VoIP phones, wireless access points, and even LED lighting systems. With the latest PoE standards, such as IEEE 802.3bt, cables can deliver up to 100W of power, expanding the range of devices that can be powered without separate electrical wiring.
As PoE technology becomes more common, structured cabling systems must be designed with heat dissipation and power capacity in mind. This means selecting cables with the appropriate conductor size, shielding, and insulation materials. Installers and network designers will need to stay updated on PoE-compatible cabling solutions to meet future demands.
Fiber Optic Expansion into More Environments
Fiber optic cabling was once limited to long-distance and high-budget projects, but this is rapidly changing. The falling cost of materials and growing need for ultra-fast internet are leading to increased fiber deployments in business campuses, multi-story buildings, and even residential areas.
Unlike copper, fiber optic cables are immune to electromagnetic interference and can transmit data over much longer distances without signal degradation. As internet speeds offered by ISPs increase and 5G networks are deployed, fiber will become an essential component of structured networking, complementing or even replacing traditional copper cabling in many environments.
Eco-Friendly Cabling and Sustainable Installations
With environmental concerns on the rise, manufacturers and installers are looking for ways to make cabling systems more sustainable. This includes using recyclable materials, reducing the use of PVC, and producing cables that meet RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and other green certifications.
Installers are also adopting more energy-efficient methods and minimizing cable waste by using modular designs and better planning tools. These eco-conscious practices not only reduce environmental impact but also help businesses meet regulatory and corporate sustainability goals.
Enhanced Testing and Certification Requirements
As cabling systems become more complex and performance expectations rise, rigorous testing and certification are more important than ever. Installers and IT managers must ensure that all cables meet industry standards and function optimally in real-world conditions.
This has led to the increased use of advanced testing tools that can measure attenuation, crosstalk, return loss, and other critical parameters. Manufacturers are also providing pre-terminated cable assemblies and third-party verified solutions to simplify installation and ensure reliability. The future of structured networking will rely heavily on these practices to maintain network integrity and avoid costly downtime.
Modular Cabling Systems and Easy Upgrades
Traditional cabling setups often required a complete overhaul when technology changed. But modern modular cabling systems are designed with flexibility and scalability in mind. These systems allow for easier upgrades, reconfiguration, and maintenance without disrupting the entire network.
Whether its adding a new server, integrating smart lighting, or expanding wireless access, modular cabling systems support quick changes with minimal effort. This flexibility is particularly valuable in co-working spaces, educational campuses, and data centers where technology is constantly evolving.
Supporting IoT Growth in Homes and Industries
The Internet of Things is rapidly expanding in both consumer and industrial sectors. From smart refrigerators and thermostats to factory automation sensors, the number of connected devices is growing at an unprecedented rate.
To handle this explosion of devices, structured cabling must support dense connectivity while maintaining performance. This involves not only choosing the right type of cable but also implementing layout designs that reduce interference and simplify troubleshooting. The future of data cabling will likely include innovations in connectors, patch panels, and cable management to support the IoT ecosystem.
Workplace Changes and Hybrid Networks
With the global shift toward remote and hybrid work models, businesses are rethinking their office layouts and network infrastructure. Flexibility and adaptability have become priorities, and this is influencing how structured cabling is planned and deployed.
Networks now need to support a mix of wired and wireless connectivity. Even though wireless access points are expanding, they still depend on robust wired connections in the background. Cabling infrastructure must be designed to support these hybrid networks while providing sufficient bandwidth for simultaneous video calls, cloud access, and collaboration tools.
Training and Skill Development for Technicians
As structured networking becomes more advanced, the need for skilled technicians is also growing. Installers must stay updated with new standards, technologies, and tools to deliver future-ready solutions. Industry certifications such as BICSI, CompTIA Network+, and manufacturer-specific training programs are becoming essential.
This professional development ensures that technicians can handle everything from fiber splicing and PoE installations to compliance and testing. A well-trained workforce is the foundation for successful cabling infrastructure in the future.
Role of AI and Automation in Cabling Design
Artificial intelligence is beginning to influence the design and planning of structured cabling systems. Software tools now use AI algorithms to optimize cable routing, reduce material usage, and predict performance issues before installation even begins.
Automation is also playing a role in large-scale installations where robotic tools assist with cable placement, labeling, and termination. As these technologies mature, they will significantly reduce human error and improve efficiency in cabling projects.
How Educational Resources Help Simplify Choices
For many users, selecting the right type of Ethernet cable or network configuration can be confusing. Thats why online resources, tutorials, and guides play an important role in decision-making. For example, a complete guide to using Ethernet splitters can help users understand alternative ways of expanding their connectivity without rewiring an entire system.
Such content empowers users to make informed choices, avoid common mistakes, and better maintain their network performance. As data cabling becomes more integrated into everyday technology use, accessible education will become increasingly valuable.
Conclusion: Structured Cabling Is Evolving Fast
The future of structured networking lies in intelligent, sustainable, and high-performance cabling systems. As bandwidth demands increase and networks become more complex, data cabling must evolve to keep pace. Trends like PoE, fiber optics, modular systems, and AI-driven design are reshaping how networks are built and maintained.
Investing in future-ready cabling solutions is not just about keeping up with technology its about ensuring that your network can adapt to whatever comes next. Whether you're planning a new office, upgrading a data center, or setting up a smart home, staying ahead of these trends will help you build a network thats both reliable and ready for the future.